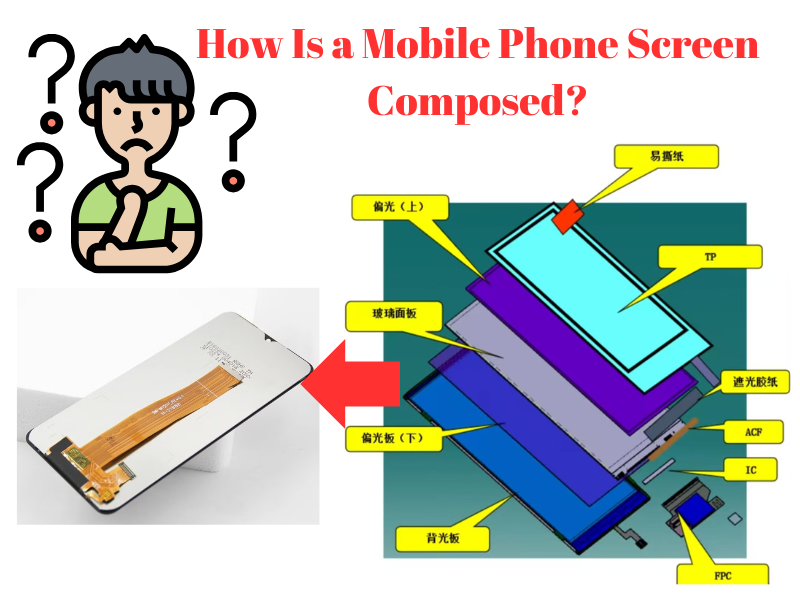
The phone screen, a key component of any smartphone, is what enables you to see and interact with your device. Whether you’re watching videos, reading, or browsing, the screen’s functionality and design are crucial. But how exactly is a phone screen assembled? Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of its construction process.
1. LCD Glass: The Foundation
The first component of a phone screen is LCD glass, which serves as the base structure.
- Two Faces of the Glass:
- TF (Thin Film) Side: The front face, responsible for displaying the visuals.
- TFT (Thin Film Transistor) Side: The back face, responsible for transmitting signals to pixels.
This dual-layer design ensures the screen can efficiently display content while maintaining structural integrity.
2. Applying Polarizers
To enhance the screen’s visual output, polarizers are applied to both sides of the LCD glass.
- Upper and Lower Polarizers: These layers filter light and optimize its alignment, improving image clarity and brightness.
- Purpose: They enable the display to show videos and images with better pixel precision and vibrancy.
3. Adding the Driver IC and Forming the FPC Module
The Driver IC (Integrated Circuit) acts as the brain of the screen, controlling the pixels.
- Driver IC Installation: It is attached to the LCD glass, typically on a layer known as the ITO (Indium Tin Oxide).
- FPC Module Formation: After installing the IC, the Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) is added to form a module. This module drives the glass pixels, allowing the screen to function effectively.
4. Applying OCA Optical Adhesive
Once the module is ready, OCA (Optical Clear Adhesive) is used to bond the layers.
- Role of OCA:
- It ensures high optical transparency, reducing glare and maintaining display clarity.
- It also strengthens the screen structure by securely attaching its layers.
5. Attaching the Cover Plate
The cover plate is the outermost protective layer of the screen.
- Purpose:
- It determines the screen’s shape and protects internal components.
- It also serves as the touch interface, allowing users to interact with the device.
The cover plate is often made of strengthened glass, like Gorilla Glass, to resist scratches and damage.
6. Installing the Backlight (BL)
The backlight (BL) is an essential component that provides illumination to the screen.
- Function:
- Without a backlight, the LCD screen would be dark and unreadable.
- The backlight evenly lights up the display, ensuring clear visibility under different lighting conditions.
- Type: LED backlights are commonly used for their efficiency and brightness.
7. Connecting the Ribbon Cable
The final step involves connecting the screen to the phone’s mainboard via a ribbon cable.
- Purpose:
- It transmits touch signals from the screen to the motherboard.
- It also carries data to display visuals and ensures seamless communication between the screen and the device.

Summary
A phone screen is made up of several carefully assembled components, each playing a vital role in its functionality. From LCD glass and polarizers to the driver IC, OCA adhesive, cover plate, backlight, and ribbon cable, each step ensures the screen delivers a clear, responsive, and durable display. Understanding this process gives us greater appreciation for the technology we use daily.